AI Atlas #13:
AI Agents
Rudina Seseri
🗺️ What are AI Agents?
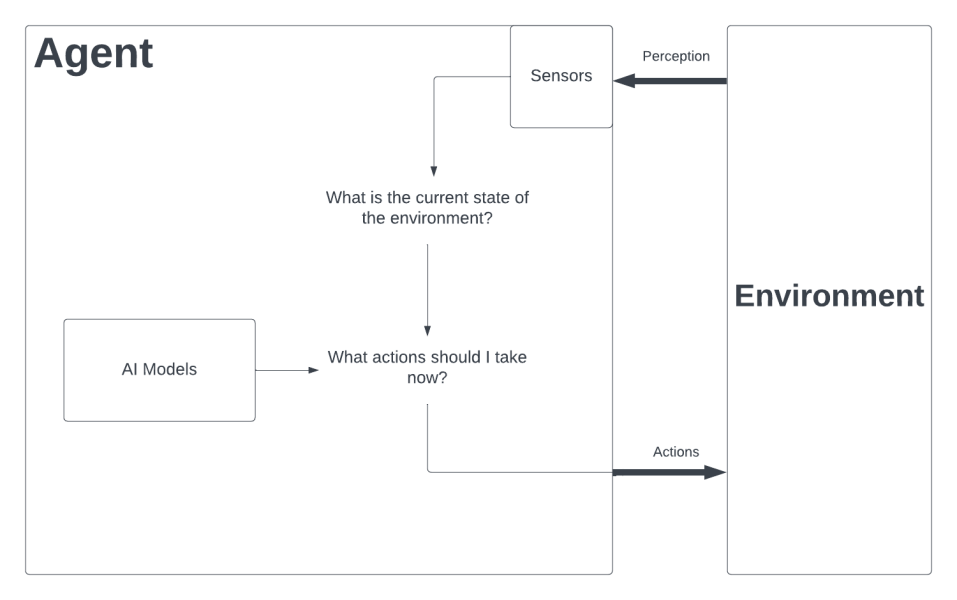
AI agents are intelligent software systems designed to perceive their environment, reason about it, make decisions, and take actions to achieve specific objectives autonomously. They incorporate various AI techniques such as natural language processing, machine learning, and computer vision to interact with users and understand their needs. AI agents can operate autonomously or in collaboration with other agents or human users, enabling them to solve complex problems and adapt to dynamic domains.
Meta AI’s CICERO, first announced in November of 2022, represents a notable demonstration of the capabilities of AI agents in the areas of strategic reasoning and natural language processing. It is an AI agent that can play the strategy game Diplomacy at a human level. The model is able to play this complex strategy game alongside humans at a highly-skilled human-level performance leveraging strategic reasoning and natural language processing. While this demonstration was in the form of a classic strategy board game, the capabilities have implications across markets and enterprise needs.
Strategic reasoning refers to the ability of an agent to analyze the current state, anticipate future scenarios, and devise long-term plans to achieve its objectives effectively. It enables decision-making across domains and planning over extended periods or in complex environments. In the case of CICERO, this means that the AI agent is capable of assessing the current state of the game, predicting how other players will move, and making plans that will give CICERO the best chance of winning.
Natural language processing is the ability to understand and generate human language. This enables AI agents to process and understand human language in various forms, such as text or speech, and effectively communicate with users, such as a business user interacting with an AI platform. In the case of CICERO, this means being able to read and write messages to other players, negotiate alliances, and build trust.
AI Agents typically leverage AI to enable capabilities such as:
Perception: AI Agents gather information about their environment through sensors or by receiving input from external sources such as databases. These sensors could be cameras, microphones, or other means of data collection.
Reasoning: AI Agents use reasoning and inference techniques to interpret and process the information received from their environment. They analyze and understand the data to make informed decisions.
Decision-making: Based on their perception and reasoning, AI agents determine the best course of action to achieve their goals. This may involve evaluating different options and selecting the most appropriate action.
Action: AI Agents execute the chosen action in their environment using actuators, devices that convert signals into physical actions, or by interacting with external systems. These actions can be physical movements, generating output, or making decisions that affect the environment.
Learning: Many AI agents incorporate learning capabilities to improve their performance over time. They can learn from their experiences, adapt to changing circumstances, and refine their decision-making processes.
🤔 Why AI Agents Matter and Their Shortcomings
AI agents have numerous significant implications including:
Improved efficiency: AI agents can automate tasks that are repetitive, time-consuming, or dangerous. This can free up humans to focus on more creative and strategic work.
Better decision-making: AI agents can help businesses to make better decisions by analyzing large amounts of data and identifying patterns.
Improved customer service: AI agents can help businesses provide better customer service by answering questions, resolving issues, and providing support without costly and time-consuming human intervention.
New opportunities: AI agents can create new opportunities for businesses and individuals. For example, AI agents can be used to develop new products and services or even create new jobs as they offer humans previously unattainable abilities.
AI at Meta’s CICERO specifically demonstrates the power of AI agents to learn and adapt. By combining natural language processing, which enables the agents to communicate naturally with humans, and strategic reasoning, which allows the model to collaborate or compete against humans, CICERO demonstrates a revolution in human-machine collaboration.
As with all breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, there are limitations or areas for caution with AI agents, including:
Job Displacement: AI agents could lead to job displacement in some sectors, such as manufacturing and customer service, and thus must be developed alongside effective retraining and reskilling.
Security risks: AI agents could be used for malicious purposes, such as cybercrime, and thus increase the capabilities of bad actors.
Ethical concerns: AI agents raise new ethical concerns, such as the potential for bias and discrimination, as their decisions are only as unbiased and ethical as the data they are trained on and can be made autonomously, without human intervention to ensure they are made without bias. Thus, explainability in AI Agent decision-making must be emphasized as the technology advances.
🛠 Uses of AI Agents
AI Agents have numerous use cases including:
Manufacturing: AI agents can be used to operate machines, inspect products, and manage inventory supplementing human labor and automating strenuous or dangerous tasks. For example, collaborative robots on a production floor can work alongside human operators, performing tasks such as assembly, pick-and-place operations, quality control, or material handling.
Sales and marketing: AI agents can be used to generate leads, qualify prospects, and close deals by collaborating with human sales teams or, potentially, as a team of autonomous agents. For example, AI agents could work alongside SaaS sales representatives and account executives to recommend the most valuable software offerings based on customer needs and product documentation or even support implementation by interacting with the integration software and writing code.
Security: AI agents can be used to not only detect but also autonomously prevent security threats, identify potential security vulnerabilities, and develop security solutions. For example, an enterprise Security Operations Center (SOC), which is often overwhelmed by potential threats, could be “staffed” by a team of human analysts and AI Agents.
Customer service: AI agents can be used to not only answer customer questions but resolve their problems and provide live support. For example, an AI agent deployed on an e-commerce site can track down a lost item by collecting information from a user in natural language, utilizing the e-commerce company’s customer and product database, and interacting with the correct shipping and logistics provider (ex: UPS, FedEx) software much like a human representative would.
Product development: AI agents can gather customer feedback and use logic and reasoning to identify new product opportunities or even develop new features and products. For example, AI agents can simulate and conduct virtual testing, reducing the need for physical prototypes and accelerating the development timeline.
AI agents hold tremendous potential for the future as they continue to advance in learning, adaptability, and natural language understanding. They have the potential to deliver much higher productivity and to do good, including augmenting human intelligence, facilitating collaboration, and addressing ethical considerations, leading to more sophisticated and trustworthy systems that positively impact various domains.